Insight Factory Background Jobs Scheduler
This tool allows to schedule and execute background tasks called jobs for Insight Factory needs. Under the hood it is based on the Hangfire background service.
Prerequisites
Only two things are required to run the Background Jobs Scheduler:
- ASP.NET Core Runtime - it allows to run Background Jobs Scheduler application
- Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 or newer - it is used as a background jobs storage
Hangfire Dashboard
Background jobs can be viewed and managed through the Hangfire Dashboard. It is accessible from the browser under the Background Jobs Scheduler /hangfire page.
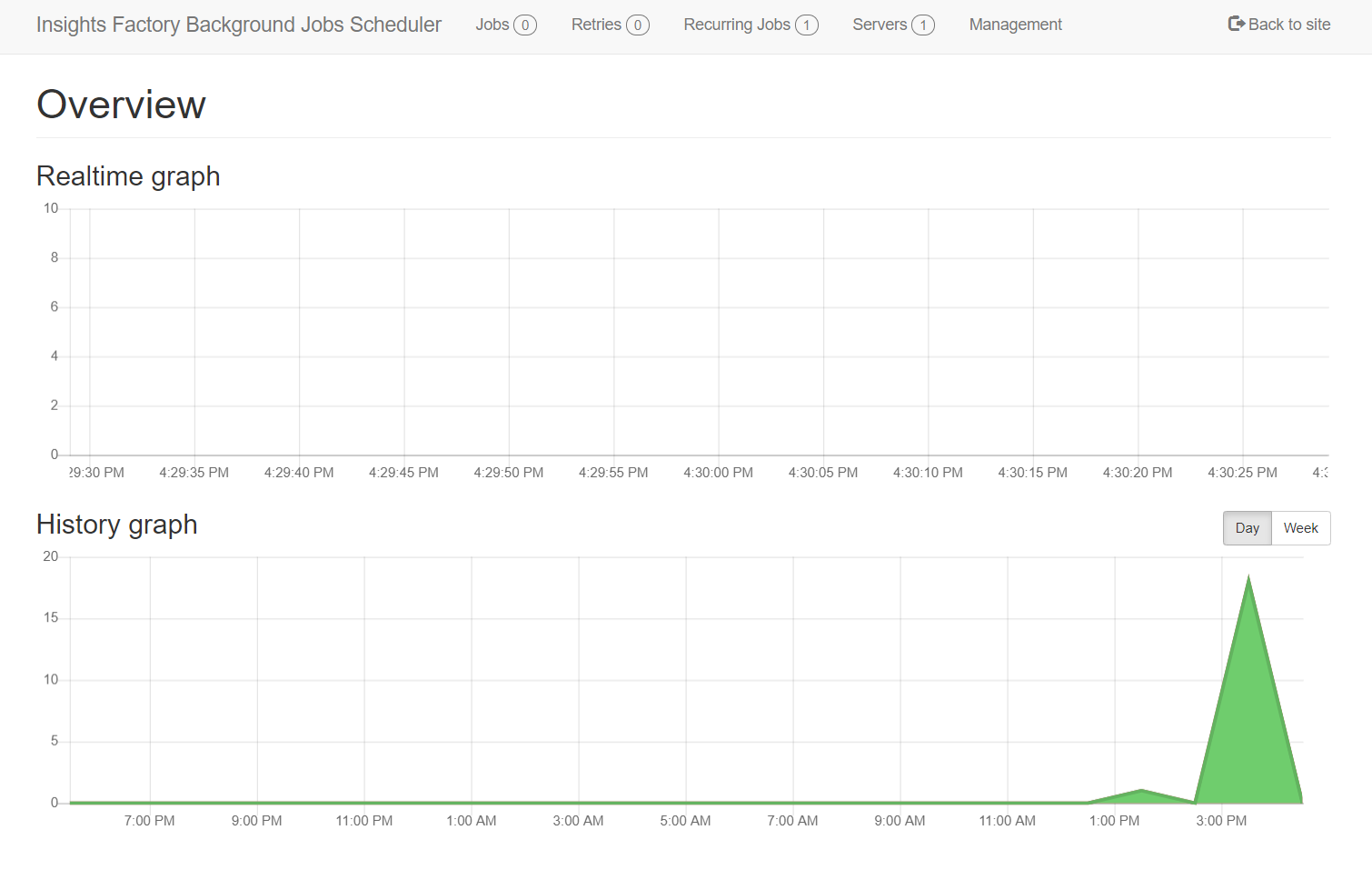
Example job
The functionality of the Dashboard in this documentation is demonstrated using an example of a sample job - Scheduled Insights Definition Job. This job, when executed, sends a message to the Insight Definition Scheduler node, which starts processing Scheduled Insights Definitions.
Background job types
First of all, there are a four ways in which background jobs can be triggered:
- Immediate - triggers a job as soon as it is added to the job list (queue).
- Scheduled - starts a job at a specific date and time.
- Delayed - starts the job after a certain period of time.
- Repeating (recurring jobs) - runs the job periodically according to the specified CRON expression.
Managing background jobs
All available background jobs are defined on the Management page. Each job can be managed by selecting its name in the left panel. In the selected job, its configuration will appear. If the job has any parameters, they can be configured here along with the job type.
Once all the job properties have been configured, the job can be added to the queue by using the appropriate Execution button.
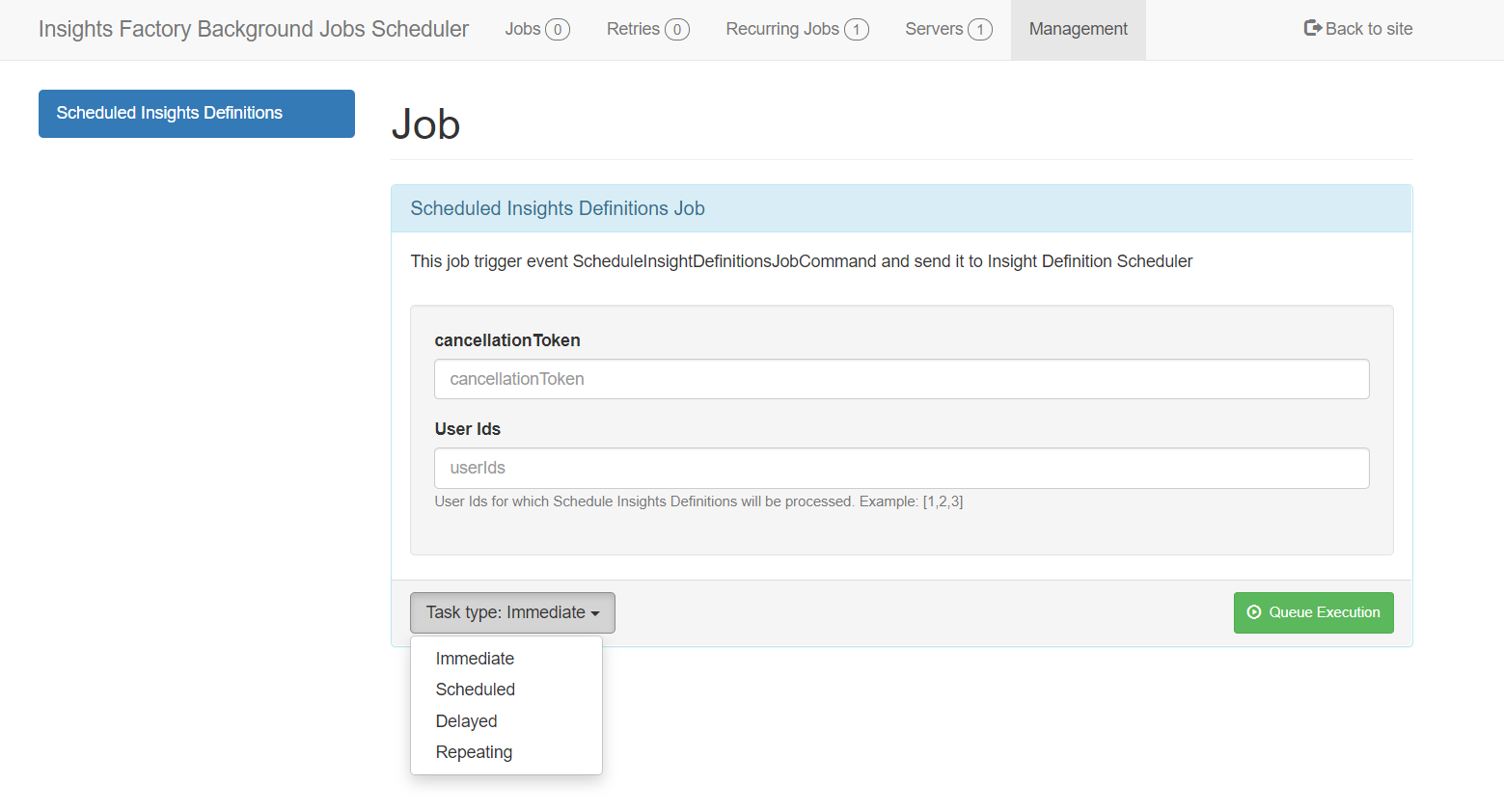
Jobs overview
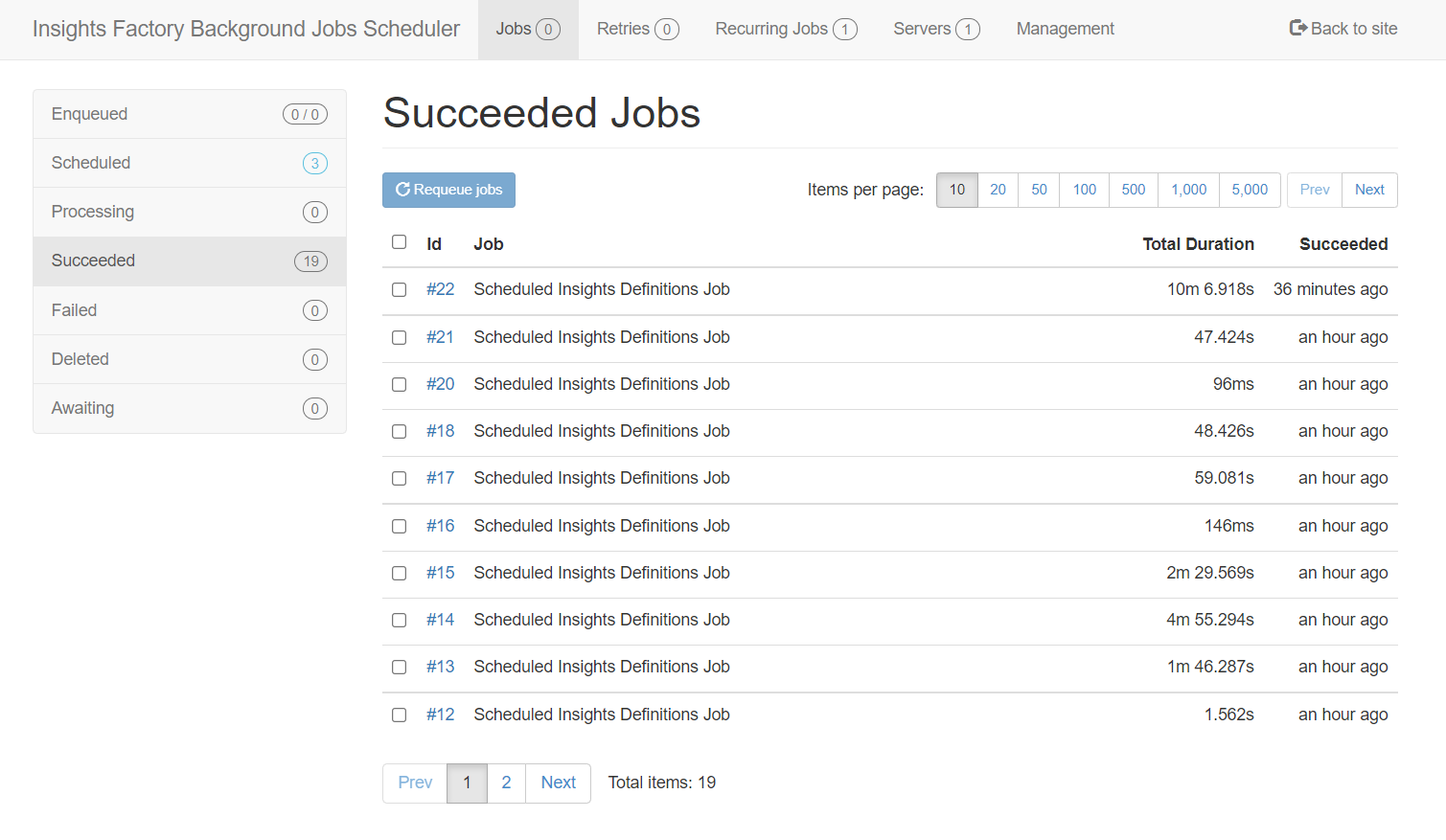
Queued jobs and their status can be seen on the Jobs page. The page consists of subpages on which you can see the status of jobs depending on their statuses.
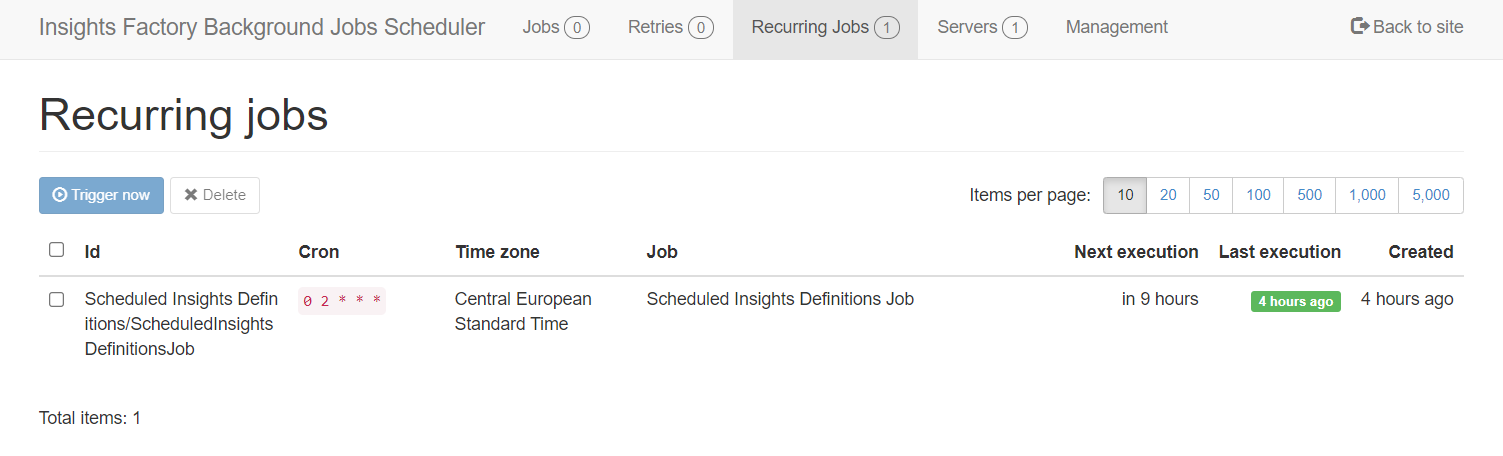
Managing Recurring Jobs
Repeating jobs will also be visible on Recurring Jobs page. This page allows you to delete recurring jobs.
Note: editing a recurring job is accomplished by overwriting it on the Management page by selecting the
Repeatingjob type and usingId(from Recurring Jobs page) as theJob Name.
Default jobs
Background jobs for Insight Factory are predefined and provided out of the box. Their configuration is defined in the appsettings.json file under the Jobs -> Default[] node and looks as follows:
"Jobs": {
"Default": [
{
"id": "Scheduled Insights Definitions/ScheduledInsightsDefinitionsJob",
"cron": "0 12 * * *",
"handler": "Meniga.BackgroundJobsScheduler.ScheduledInsightsDefinitions.Job, Meniga.BackgroundJobsScheduler",
"handlerMethod": "Execute",
"enabled": true
}
]
},
Note:
Default[]node is an array and other default jobs can be defined in it.
Detailed configuration
Each default job should be configured according to the following parameters. For now, only recurring jobs can be defined as default jobs.
id- unique Job Id (string)cron- Define when job should be fired. This is a CRON expressions according to the following format https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cron#CRON_expressionhandler- qualified assembly name for the job handler. Only handlers defined in Background Jobs Scheduler can be used. For exampleMeniga.BackgroundJobsScheduler.ScheduledInsightsDefinitions.Job, Meniga.BackgroundJobsSchedulerhandlerMethod- Method name defined in above job handlerenabled- If enabled job will be added at application startup
Note: a default job is added only if a job with a given
iddoes not exist. If you change the default job configuration, it will have no effect if a job with thatidexists.
Multiple instances
Background Jobs Scheduler can be run in multiple instances. The only requirement is that each instance connects to the same database. All instances are presented on the Dashboard Servers page.
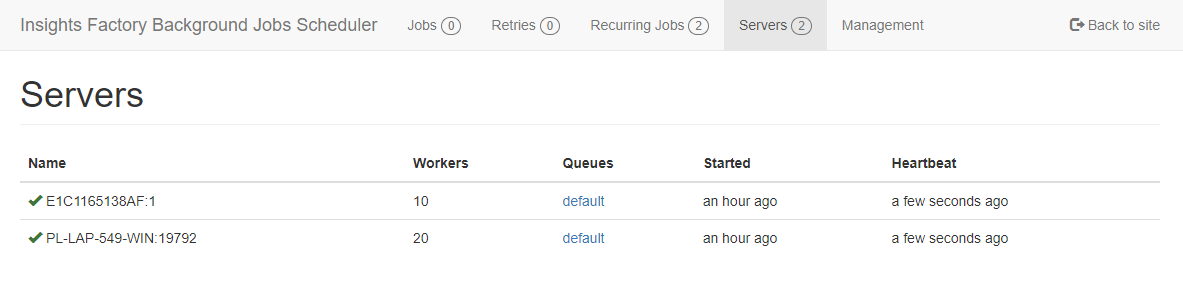
Recurring jobs are supported in multiple instances are fired only once in a given CRON occurrence.
Instances can run on systems with different time zones. In this case, jobs are triggers according to time zone defined in a job.
Note: if instances runs on system with different time zones then the job trigger date should be defined in the time zone known to each system on which Background Jobs Scheduler runs. It is recommended to use UTC time zone, which is known to all systems regardless of their time zones.